How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to intricate drone racing. Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical skill, encompassing understanding various drone types, pre-flight safety procedures, and the nuances of flight controls. This guide provides a structured approach to learning, progressing from basic maneuvers to more advanced techniques, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience.
We’ll explore different drone models, comparing their capabilities and operational characteristics. Crucially, we’ll emphasize the importance of safety and legal compliance, covering pre-flight checks, airspace regulations, and ethical considerations. By the end, you’ll possess the foundational knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly and creatively.
Drone Types and Their Operation

Understanding the different types of drones and their operational characteristics is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will explore various drone designs, their flight controls, pre-flight checks, and key features.
Drone Classifications and Operational Characteristics
Drones are categorized primarily by their rotor configuration. Quadcopters, with four rotors, are the most common, offering excellent stability and maneuverability. Hexacopter drones, featuring six rotors, provide increased redundancy and payload capacity, making them suitable for heavier equipment. Fixed-wing drones, resembling airplanes, are generally faster and have longer flight times but require runways for takeoff and landing. Multirotor drones (quadcopters, hexacopters, etc.) offer vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) capabilities, simplifying operation in various environments.
Flight Controls and Functionalities
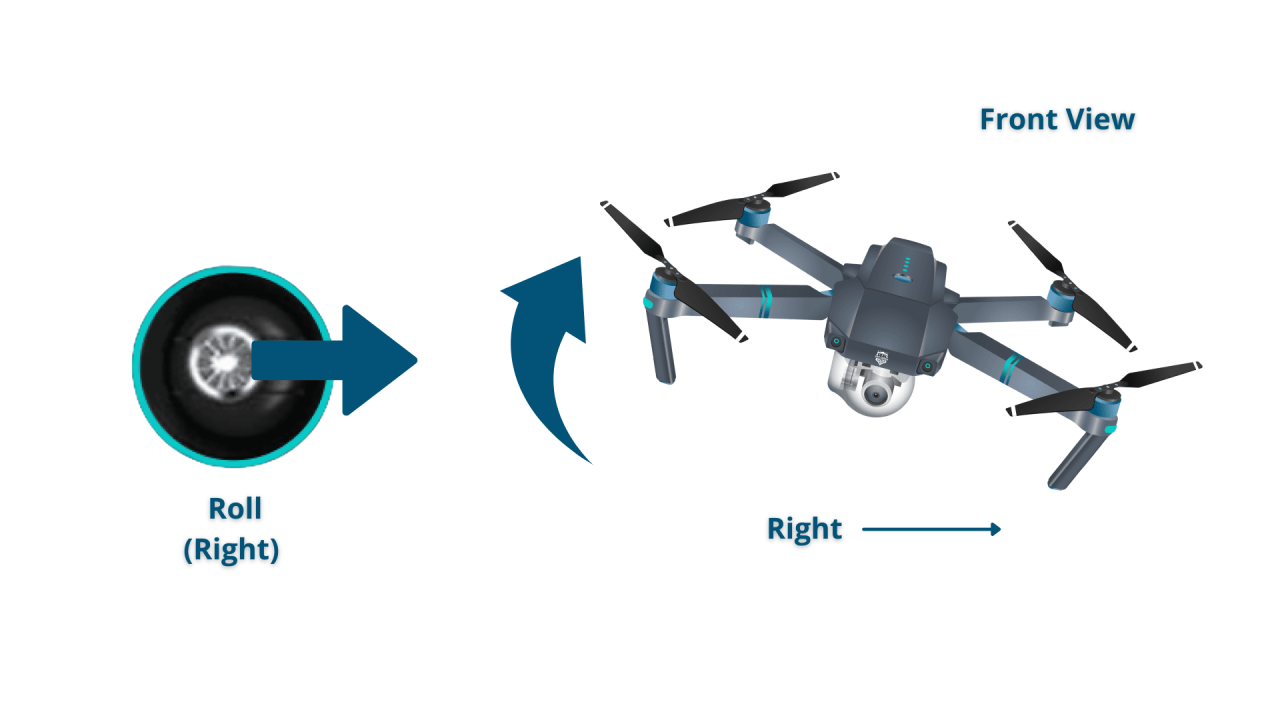
While specific controls vary between manufacturers and models, most drones use joysticks for directional control and switches or dials for functions like camera control and flight modes. Quadcopters generally use two joysticks: one for yaw (rotation) and throttle (altitude), and the other for pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right). Hexacopter controls are similar, though often with added functionality due to the extra rotors.
Fixed-wing drones typically use a more complex control system, often mimicking the controls of a traditional aircraft.
Pre-Flight Checks for Different Drone Types
Pre-flight checks are essential regardless of drone type. However, some checks are more critical for specific designs. For all drones, visual inspection of rotors, propellers, and body for damage is vital. Battery levels should always be checked, and GPS signal strength is crucial, especially for autonomous flight modes. For fixed-wing drones, runway conditions and wind speed assessment are added pre-flight considerations.
Comparison of Popular Drone Models
| Feature | DJI Mavic 3 | DJI Phantom 4 Pro V2.0 | Autel Evo II Pro |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (g) | 895 | 1388 | 1060 |
| Battery Life (min) | 46 | 30 | 40 |
| Camera Quality (MP) | 20 (main) + 12 (tele) | 20 | 48 |
| Range (km) | 15 | 7 | 9 |
Pre-Flight Procedures and Safety Checks
A thorough pre-flight checklist ensures safe and legal operation. This section details essential steps, safety best practices, and regulatory considerations.
Step-by-Step Pre-Flight Inspection Checklist
- Inspect the drone for physical damage.
- Check battery level and charge.
- Verify GPS signal strength.
- Calibrate the compass.
- Review local regulations and airspace restrictions.
- Choose a safe and legal flight location.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Perform a pre-flight calibration (if needed).
Best Practices for Safe Drone Operation
Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone. Avoid flying near airports, power lines, or crowds. Be mindful of wind conditions and never fly in adverse weather. Understand and adhere to all local regulations and airspace restrictions. Regularly inspect and maintain your drone to prevent malfunctions.
Understanding Local Regulations and Airspace Restrictions, How to operate a drone
Drone regulations vary significantly by location. Before flying, always check with your local aviation authority (e.g., FAA in the US, CAA in the UK) to ensure compliance. Airspace restrictions, such as those around airports or other sensitive areas, must be strictly observed. Failing to comply can result in fines or legal action.
Pre-Flight Sequence Flowchart
A visual flowchart would illustrate the steps above, starting with pre-flight checks, then calibration, GPS signal verification, and finally, confirmation of legal compliance before initiating the flight.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
This section covers fundamental drone controls and maneuvers, enabling you to safely operate your drone. Mastering these basics is essential before attempting more advanced techniques.
Drone Controller Functions
Most drone controllers have two joysticks. One typically controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the other controls pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right). Buttons and switches on the controller activate functions like camera control, return-to-home, and flight modes. Understanding the function of each control is paramount for safe and effective flight.
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Takeoff and landing are initiated using the throttle stick. Hovering involves maintaining a stable altitude and position using fine adjustments to the control sticks. Directional movement involves manipulating the pitch and roll sticks to move the drone forward, backward, left, or right. Smooth, controlled movements are achieved through gentle and precise control stick adjustments.
Tips for Smooth and Controlled Flight
Start with practice in a wide-open space, away from obstacles. Begin with slow, deliberate movements, gradually increasing speed and complexity as you gain confidence. Practice hovering until you can maintain a stable position. Use the return-to-home function to practice retrieving the drone in case of loss of control.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a good grasp of regulations and safety procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, safe and responsible drone piloting hinges on thorough knowledge and practice.
Successful Drone Takeoff and Landing Steps
- Ensure pre-flight checks are complete.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Wait for GPS signal acquisition.
- Gently raise the throttle stick to initiate takeoff.
- Maintain a stable hover.
- For landing, gently lower the throttle stick.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Advanced Flight Techniques: How To Operate A Drone
Once comfortable with basic flight, you can explore more advanced maneuvers and flight modes. This section will cover advanced techniques, GPS utilization, and navigating challenging conditions.
Complex Maneuvers and Precise Positioning
Advanced maneuvers, such as flips and rolls, require practice and precise control. These maneuvers are typically activated using buttons or switches on the controller and often require specific flight modes. Precise positioning, particularly important for photography and videography, often relies on GPS and intelligent flight modes.
GPS and Autonomous Flight Modes
GPS enables features like return-to-home, which automatically returns the drone to its starting point. Autonomous flight modes, such as point-of-interest (POI) orbits or waypoints, allow for pre-programmed flight paths. These modes require a strong GPS signal and careful planning to ensure safe operation.
Navigating Challenging Environments
Windy conditions can make controlling a drone difficult. Flying in confined spaces requires extra caution and precise control. Understanding the limitations of your drone and adjusting your flight techniques accordingly is crucial for safe operation in these environments.
Flight Modes and Functionalities
| Flight Mode | Description | Use Cases | Safety Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beginner Mode | Limits speed and responsiveness | Training, beginners | May restrict maneuverability |
| Sport Mode | Increased speed and responsiveness | Experienced pilots, dynamic shots | Increased risk of loss of control |
| GPS Mode | Uses GPS for stability and position holding | Stable shots, autonomous flight | Requires strong GPS signal |
| Return to Home (RTH) | Automatically returns drone to home point | Emergency situations, battery low | Ensure clear path for return |
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
This section explores camera settings, composition techniques, and parameter adjustments for capturing high-quality aerial footage.
Camera Settings and Image Quality
Understanding camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture is vital for achieving optimal image quality. Higher ISO values improve low-light performance but can introduce noise. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion but require more light. Aperture controls depth of field, influencing background blur.
Composing Compelling Aerial Shots
Aerial photography and videography benefit from careful composition. The rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetrical compositions are all applicable. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to create visually engaging content. Consider the lighting and time of day to enhance your shots.
Adjusting Camera Parameters

Exposure compensation adjusts overall brightness. Focus can be adjusted manually or automatically, depending on the drone and camera system. White balance corrects color casts due to different lighting conditions. Understanding these parameters allows for precise control over image quality.
Camera Angles and Applications
High-angle shots provide a wide overview, ideal for landscapes. Low-angle shots create a dramatic perspective, emphasizing scale and detail. Side angles can capture movement and texture. Experimentation with different angles enhances the visual storytelling of your aerial footage.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting skills are essential for prolonging the life of your drone and ensuring its reliable operation.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule should include inspecting propellers, motors, and body for damage. Clean the drone after each flight to remove dirt and debris. Check and clean the camera lens. Inspect and clean the gimbal, if applicable. Store the drone and batteries properly to prevent damage.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Common malfunctions include motor failure (often due to damage or wear), GPS signal loss (due to interference or obstructions), battery issues (low charge or damage), and camera malfunctions (lens dirt or internal problems). Understanding potential causes helps in efficient troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Troubleshooting steps often involve visual inspection for physical damage, checking battery levels and connections, and ensuring a clear GPS signal. If problems persist, consulting the drone’s manual or seeking assistance from the manufacturer or a qualified technician may be necessary.
Essential Tools for Drone Maintenance
- Screwdrivers (various sizes)
- Propeller balancer
- Cleaning cloths and solutions
- Multi-meter
- Spare parts (propellers, screws)
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to legal and ethical guidelines. This section explores privacy concerns, legal requirements, and potential consequences of non-compliance.
Respecting Privacy and Avoiding Unauthorized Surveillance
It’s crucial to respect individuals’ privacy and avoid unauthorized surveillance. Never fly your drone over private property without permission. Be mindful of recording individuals without their consent, as this can have legal implications.
Legal Requirements for Drone Operation
Drone regulations vary by jurisdiction. These regulations often cover registration requirements, flight restrictions (no-fly zones), licensing, and operational limitations. Failing to comply can result in significant penalties.
Potential Legal Consequences of Violating Drone Regulations
Violating drone regulations can lead to fines, license suspension, or even criminal charges, depending on the severity of the violation. Understanding and adhering to all relevant regulations is crucial to avoid legal consequences.
Key Legal Considerations for Drone Operation
| Jurisdiction | Registration | Licensing | Flight Restrictions |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States (FAA) | Required for most drones | May be required depending on use | Numerous no-fly zones and airspace restrictions |
| United Kingdom (CAA) | Required for most drones | Optional, but recommended for commercial use | Airspace restrictions around airports and sensitive areas |
| [Other Jurisdiction] | [Information specific to the jurisdiction] | [Information specific to the jurisdiction] | [Information specific to the jurisdiction] |
Drone Battery Management and Safety
Proper battery management is crucial for safe and efficient drone operation. This section details safe charging, storage, and disposal practices.
Proper Battery Charging and Storage
Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow the charging instructions carefully. Avoid overcharging or discharging batteries, as this can damage them and potentially lead to fire hazards. Store batteries in a cool, dry place, away from flammable materials.
Risks Associated with Damaged or Improperly Handled Batteries
Damaged or improperly handled drone batteries can overheat, catch fire, or explode. Never puncture or crush a battery. Avoid exposing batteries to extreme temperatures or moisture. If a battery shows signs of damage, dispose of it properly.
Safe Disposal Procedures for Drone Batteries
Drone batteries should be disposed of according to local regulations. Many jurisdictions have specific guidelines for the disposal of lithium-ion batteries. Check with your local waste management authority for proper disposal instructions. Improper disposal can harm the environment.
Best Practices for Extending Battery Life
Avoid extreme temperatures during charging and storage. Store batteries at a moderate charge level (around 50%) when not in use. Avoid fully discharging batteries repeatedly. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for battery care to maximize lifespan.
Operating a drone successfully involves a combination of technical understanding, responsible piloting, and adherence to regulations. From mastering basic flight controls to understanding advanced techniques and camera operation, this guide has provided a structured pathway to becoming a competent drone pilot. Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to refining your skills and expanding your aerial capabilities. Always prioritize safety, respect airspace restrictions, and enjoy the incredible perspectives that drone flight offers.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the best drone for beginners?
Several user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring features like GPS stabilization and automated flight modes. Research models known for their ease of use and robust build quality.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning the basics is crucial for safe and effective operation; for a comprehensive guide, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone which covers everything from takeoff to landing procedures. Safe and responsible drone piloting requires understanding these fundamental techniques.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration is crucial for accurate flight. It’s recommended to calibrate before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant impacts.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
If signal loss occurs, most drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If RTH fails, visually locate the drone and attempt to regain control. If unsuccessful, report the loss to relevant authorities.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country/region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific regulations and registration procedures. Failure to register can result in penalties.
